A Brief Guide to Microsoft Power BI (with Frequently Asked Questions)
With its proven track record in the field of tech, Microsoft launched its compelling analytics tool—the Power BI. Since its release, the tool has been helping enterprises to visualize and analyze their enterprise data easily for transform their operations.
Business Intelligence or BI has proven to be essential in helping companies boost their productivity on massive scales. With that said, Power BI helps manage all facets of a company, be it logistics or human resources or customer relations, in a rather seamless manner. If that term did not ring a bell, this blog will help you understand what is Power BI and what is Power BI used for.
Before we understand Power BI and its various verticals, let us learn what is BI. (Keep reading till the end to find answers to some of the most frequently asked questions on Power BI.)
Contents
# What is Business Intelligence?
BI or Business Intelligence is a technology-driven method. It helps analyze data and provides actionable information that helps corporate executives, business managers, and others make informed business decisions. Basically, BI is a set of concepts, systems, and technology that converts raw data into useful information. It is a suite of software and services that helps transform data into actionable intelligence and knowledge.
Speaking of its influence, BI directly impacts an organization’s strategic, tactical and operational business decisions. It supports fact-based decision-making by using historical data instead of assumptions and gut feelings. BI tools perform data analysis and create reports, dashboards, maps, graphs and charts to provide detailed intelligence to users about the nature of the business.
For the functioning of an organization, business intelligence plays a vital role in its operations as well as development as it helps
-
- Create KPI based on past data
- Identify and set benchmarks for varied processes
- Identify market trends and spot business problems that need addressing
- Helps with data visualization that enhances data quality, thus enhancing the quality of decision making
BI systems can be used by large enterprises as well as by small and medium-sized enterprises.
Now that we have learned what a business intelligence system is, let us learn what Power BI is.
What is Microsoft Power BI?
Power BI is an interactive data visualization software product that primarily focuses on business intelligence. It is a part of the Microsoft Power Platform. Power BI is basically a collection of software services, apps, and connectors that work together to convert unrelated sources of data into coherent, visually immersive and interactive insights. In such cases, data may be input by reading directly from a database, webpage, or structured files such as spreadsheets, CSV, XML and JSON.
Power BI is a business intelligence platform that provides non-technical business users with tools for aggregating, analyzing, visualizing, and sharing data. For users familiar with Microsoft Excel, it offers a fairly intuitive user interface. Moreover, its integration with other Microsoft products makes it a versatile self-service tool that only requires a little training upfront.
In other words, Power BI is a business intelligence and data visualization tool that is mostly used for converting data from various other data sources into interactive dashboards and analysis reports. It also offers cloud-based services for interactive visualizations with a simple interface for end-users to help them create their own reports and dashboards.
There are various versions of the Power BI available. These include desktop, service-based (SaaS) and mobile Power BI apps that are used for different platforms. The tool provides multiple software connectors and services for business intelligence purposes.
“Connect to and visualize any data using the unified, scalable platform for self-service and enterprise business intelligence (BI) that’s easy to use and helps you gain deeper data insight.” – Microsoft
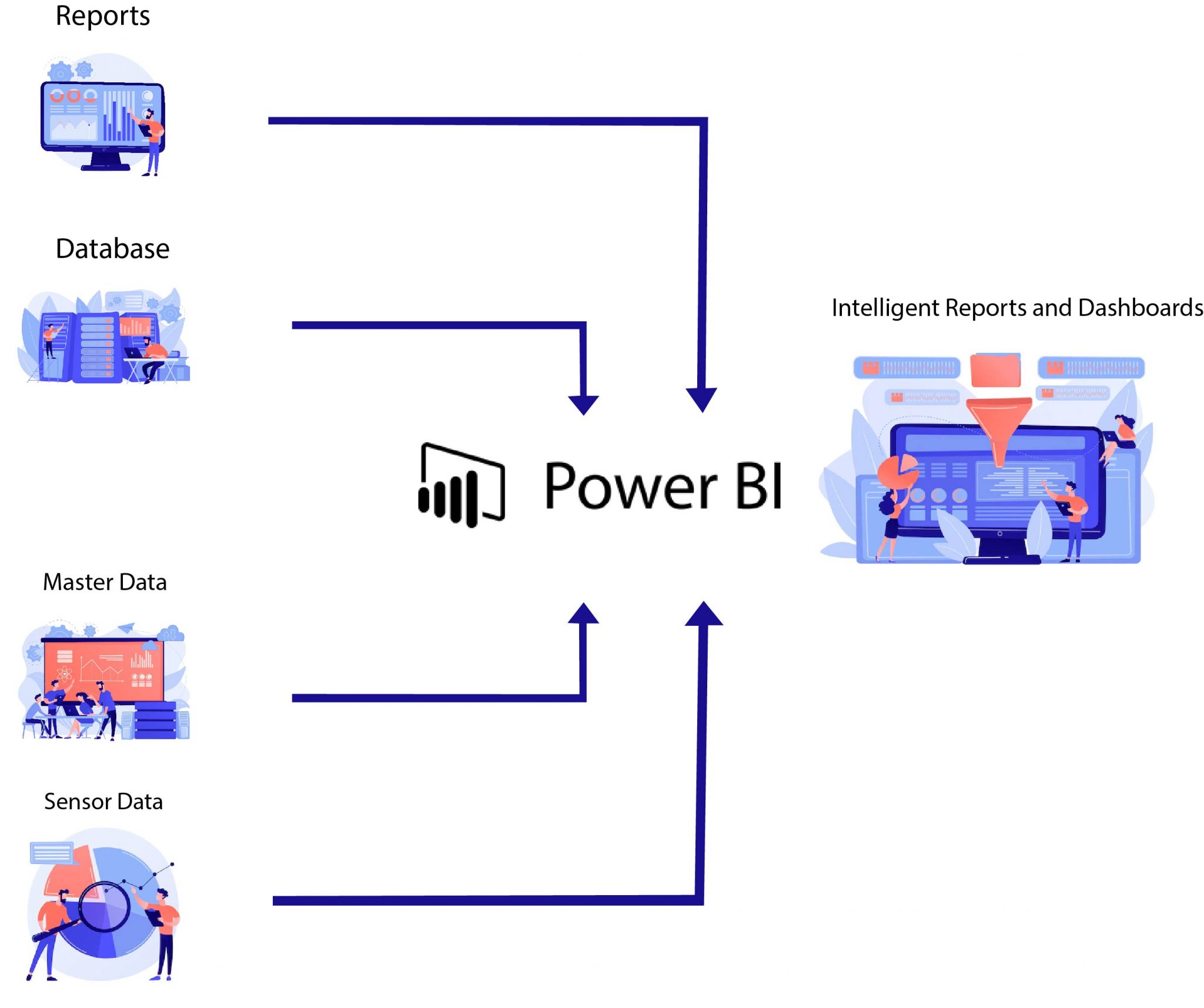 To summarize it, you can connect with the following data sources using Power BI connectors:
To summarize it, you can connect with the following data sources using Power BI connectors:
-
- Files (e.g. excel .xlsx, .pdf, .csv, .xml, .json)
- Data Bases (e.g. MS SQL, Oracle, SAP HANA, PostgreSQL, MySQL, Amazon Redshift, Snowflake, others)
- Folders (cloud-based e.g. SharePoint and locally-based)
- Azure Services (Azure SQL Database, Azure Blob Storage, Azure Data Lake, others)
- Online Services (e.g. Microsoft Exchange, Dynamics 365, Salesforce Objects, Google Analytics)
- Other Sources (e.g. websites, OData feed, ODBC, Active Directory, others)
- Indirect connection via other services (e.g. Microsoft Azure Data Factory)
The data is processed and transformed with Power BI queries to the apparent data model. The data objects required to be a part of a Power BI report are created in the form of measures, calculated columns and parameters. So, how was Power BI developed?
History of Microsoft Power BI
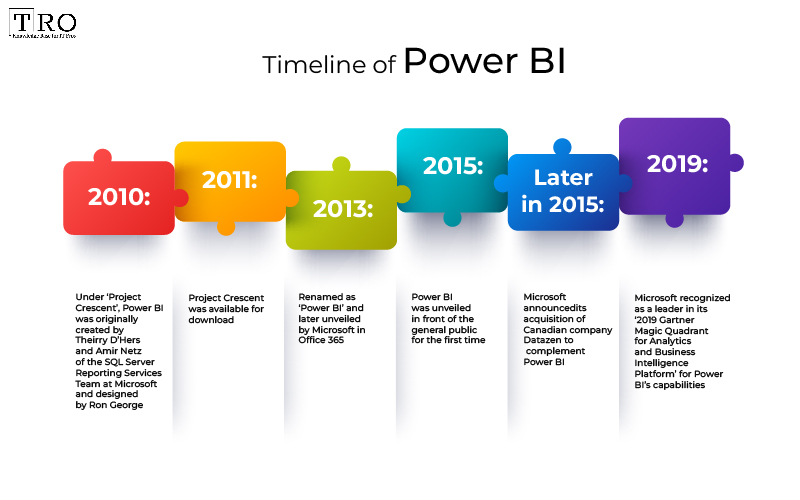
The Microsoft Power BI was originally created by Theirry D’Hers and Amir Netz of the SQL Server Reporting Services Team at Microsoft. It was originally designed by Ron George in the summer of 2010 under a project named ‘Project Crescent’ that was initially available for download in 2011. Moreover, it was initially bundled with SQL Server Codename Denali.
In 2013, it was renamed ‘Power BI’ and was later unveiled by Microsoft in Office 365. Its first release was based on the Microsoft Excel-based add-ins, which included Power Query, Power Pivot and Power View. Over time, Microsoft added various additional features such as Questions and Answers, enterprise-level data connectivity and security options via Power BI Gateways.
In 2015, the Power BI was first unveiled in front of the general public. Later in the same year, Microsoft announced that it had acquired the Canadian company, Datazen, to “complement our Power BI, our cloud-based business analytics service, rounding out our mobile capabilities for customers who need a mobile BI solution implemented on-premises and optimized for SQL Server.” In fact, most of the visuals in Power BI started life as Datazen visuals.
Further, in February of 2019, Gartner.com confirmed Microsoft as a leader in its ‘2019 Gartner Magic Quadrant for Analytics and Business Intelligence Platform’ due to the capabilities of the Power BI platform. The achievement emerged as the 12th consecutive year of recognition of Microsoft as a leading vendor in the Magic Quadrant category (3 years prior to the creation of Power BI).
What is Power BI Used For?
Microsoft’s Power BI is primarily used to find insights into an organization’s data. The tool can help connect disparate data sets, transform and clean the data into a data model and further create charts or graphs to provide visuals of the data. All of these aspects can be shared with other Power BI users within the organization.
The data models created using Power BI can be used in various ways for organizations. These include narrating stories through charts and data visualizations, examining questionable scenarios within the data, and many more. The reports generated can answer questions in real-time and help with forecasting to ensure departments fulfill their business metrics.
Additionally, Power BI also offers executive dashboards for administrators and/or managers. As a result, it helps the management to provide more insights into how departments are functioning.
Although Power BI is a self-service BI tool that delivers data analytics to employees, it is mostly used by data analysts and business intelligence professionals who create the data models before disseminating reports throughout the organization. However, users who do not hail from an analytical background can still navigate Power BI and create reports. The tool is used by department representatives and management, with reports and forecasts created to aid sales and marketing reps. Meanwhile, it also provides data for management on how the department or individual employees are progressing toward their goals. Additionally, the Power BI provides an admin portal for administrators to help configure its implementation as well as its usage monitoring and licenses.
To summarize its usage and importance, Power BI helps in the below-mentioned aspects:
-
- Pre-built dashboards and reports for SaaS Solutions
- Power BI allows real-time dashboard updates
- Offers Secure and reliable connection to data sources in the cloud or on-premises
- Offers quick deployment, hybrid configuration as well as a secure environment
- Allows data exploration using natural language query
- Offers feature for dashboard visualization regularly updated with the community
What are the Key Features of Power BI?
Since its release, Microsoft has added a plethora of data analytics features to the Power BI. To date, the tech firm continues to do so. In fact, its most stable release (2.91.383.0) was updated in March 2021. However, some of the most important features of Power BI include:
-
- Artificial Intelligence where users can access image recognition and text analytics in Power BI, create machine learning models through automated machine learning capabilities and integrate with Microsoft’s Azure Machine Learning.
- Hybrid Development Support provides built-in connectors that allow the Power BI tools to connect with various data sources from various vendors like Microsoft, Salesforce, and others.
- Quick Insights allow users to create subsets of data and automatically applies analytics to the derived information.
- Power BI’s Common data model support enables the use of a standardized and extensible collection of data schemas such as entities, attributes and relationships.
- Microsoft Cortana’s integration allows users to verbally query data using natural language and access results using the AI assistive tool.
- The Customization feature allows developers to change the appearance of default visualization as well as reporting tools and import new tools into the platform.
- APIs for integration provide sample code and application performance interfaces to developers for embedding the Power BI dashboard in other software products.
- Self-service data prep enables business analysts to ingest, transform, integrate and enrich big data into the Power BI web service which can be later shared across multiple Power BI models, reports and dashboards.
- The modeling view allows users to divide complex data models by subject area into separate diagrams, select objects and set common properties multiple times, view and modify properties in the properties window and also enables to set display folders for simpler consumption of complex data models.
What are the Various Versions of Power BI?
There are several versions of Power BI available to choose from—depending on your budget, needs, and how you want to deploy it. These versions range from light use to comprehensive features, from free to premium, allowing users to choose the one that best meets their needs.
While Power BI Desktop is a Windows desktop application, the Power BI service is an online SaaS (Software as a Service) service. The Power BI app is available on iOS and Android phones and tablets. On the other hand, the Power BI Report Server is an on-premise version. Following are some of the available versions of Power BI and each version serves a different purpose.
1. Power BI Desktop
The authoring tool of Power BI, the desktop component is mainly used by the report designers to access, transform and model the data while creating measures and building the data visualizations. Power BI Desktop can be downloaded for free and it supports Windows OS.
2. Power BI Service
It is the cloud-based central hub of the Power BI solution where users can access and interact with their Power BI reports. Using this, users can also create dashboards from their reports and can use the self-service functions for editing and creating new visualizations. Users can further share the concluded insights and collaborate with co-workers on reports and dashboards. There are two ways to license Power BI Service; Power BI Pro and Power BI Premium.
-
- Power BI Pro is not much different from the Power BI Desktop and both have the same visualization options, same limits on storage and file upload size as well as the same report refresh allowance. The key difference between both versions is Pro allows you to share data, reports and dashboards with others privately (given users also have a Power BI Pro license). Moreover, the Pro version allows you to create app workspaces where you can put collections of related dashboards and reports while easily creating accessible content packs.
-
- On the other hand, Power BI Premium serves as an alternative way to access Power BI. With Premium, you pay for the amount of space and processing capacity you require for business, instead of purchasing licenses for individual users with the Power BI Pro. It has 6 capacity models—each with varying amounts of memory to allow users choose the required amount for running their Power BI platform. The Premium version is mainly for enterprise-level businesses that generate large amounts of data and require extensive access to the app.
3. Power BI Mobile
Power BI’s mobile component allows users to interact with their published reports through smartphones or tablets via a downloadable app. The Power BI Mobile provides access to reports on the fly at anywhere and at any point in time. Users can also personalize data alerts and get real-time data updates using the mobile component of Power BI. The component is supported by Windows, iOS as well as Android devices.
4. Power BI Report Server
Report Server is a server product that comes with the Power BI Premium. It enables users to use Power BI on-premise. For some businesses, uploading data to the cloud is not a feasible option due to data regulation laws applied to their industry. It could also be due to a lack of infrastructure or connectivity where they are able to reliably access SaaS platforms.
5. Power BI Embed
Lastly, Power BI Embedded enables Independent Software Vendors (ISVs) and developers to embed Power BI’s functionality and capabilities into their respective apps on a pay-as-you-go or ‘white label’ basis. Instead of building their own reporting features, users can rather add Power BI to their products and it will cater to all the reporting necessary reporting and data analysis.
The above-listed are the different versions of the Power BI available. Let us now have a look at the components of Power BI.
What are the Components that Make Power BI?
The Power BI product is made up of a number of apps. Each has its own respective features and uses. Following are the components of Power BI:
-
- Power Query is a data connection tool that lets you transform, combine, and enhance data from several sources
-
- Power Pivot is a data modeling tool for creating data models
-
- Power View is a data visualization tool that generates interactive charts, graphs, maps, and other visuals
-
- Power Map is another visualization tool for creating immersive 3D visuals
-
- Power Q&A is a question and answer engine that lets you ask questions about your data in plain language
Now that we have understood the various components of the Power BI, let us have a look at how to create a Power BI dashboard.
# How to Create a Power BI dashboard?
You can create a Power BI dashboard using the following steps:
-
- Collect and organize your data. There are various ways to import data within your organization, file directories and databases. In fact, you can also copy and paste data from an existing dataset. But in such cases, you will have to select samples and import a pre-configured dataset. Moreover, the data is imported with no editing options.
- You can find the dataset in your workspace in the Power BI service. You can easily start analyzing the data by selecting ‘Get Quick Insights’ on the menu and a dashboard will be generated while you’re working on the data.
- Select ‘Create Report’ to open the report builder. Here, you will find three elements, namely—Canvas (Remains blank until visuals are added); Visualization Pane (Used to add and edit charts); Fields Pane (Consists of a list of the fields in your dataset based on the columns).
- For building a report, you can select the relevant fields from your data or pick a visualization that is displayed on the blank canvas.
- Click on the relevant field to add a field to your report and Power BI will automatically add the field to the required area in the chart. However, you can also drag and drop fields into the axis, legend, and values area.
- The charts will start to take shape as you add the fields. If required, you can also change it by selecting another option in the Visualizations pane.
- The next step is formatting the chart. To format it, click on the ‘format’ option and you will have access to a range of options such as the size and colors of the chart, borders, tooltips, and many more.
- You can also add a title or detail to the report by clicking on the ‘Text box’ option in the top menu. You can also have a preview of the report by selecting the ‘Reading View’ to check how the report appears to others. In fact, you can add more visualizations if needed, but remember to save your work.
- Create a dashboard by selecting ‘Pin to a live page’. Next, create a dashboard by selecting ‘Pin to a live page’. You can also add the report to an existing dashboard or in fact build a new dashboard.
- Once you’re done with your work, there are several ways you can use the reports under the ‘File: Export reports to use PowerPoint or as a PDF.’ Then, Export reports to PowerPoint or PDF and embed them in a SharePoint site.
- You can personalize your display settings using the ‘View’ option at any given time as well as change the report’s size and its colors for improved readability.
Using the following steps, you can create a Power BI dashboard. There are several examples of Power BI dashboard available on the internet that you can refer for your convenience.
Frequently Asked Questions on Microsoft Power BI :

